MedFriendly®


Disk Prolapse
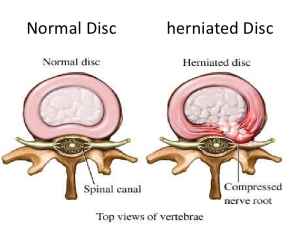
To understand disk prolapse, it is first necessary to
understand a few other terms. To begin with, vertebrae
are bones that form an opening in which the spinal cord
passes. These bones are stacked one on top of
another as shown below. Each individual bone that
makes up the vertebrae is called a vertebra. In between
the vertebrae are flat, cushiony disks (known as
intervertebral disks) that act as shock absorbers. Disk
prolapse is a painful condition of the spine in which an
intervertebral disk ruptures and part of its pulpy inside
protrudes (sticks out).
Disk prolapse shown to the right.
FEATURED BOOK: The Permanent Pain Cure for Joint Pain
WHAT ARE SYMPTOMS OF DISK PROLAPSE?
The main symptom of disk prolapse is pain, due to the protruding disk pressing on a
nerve. The pain can sometimes be so disabling that it is difficult to walk. Sometimes, the
pain can occur in the leg. This usually happens when the sciatic nerve is being pressed
on. The sciatic nerve is a long nerve that extends through the muscle of the thigh, leg,
and foot. When the sciatic nerve is pressed on, pain runs down the back of the leg from
the rear end to the ankle. This condition is known as sciatica and it can lead to weakness
of the leg if the nerve continues to be pressed on. Sciatica is sometimes accompanied by
numbness and tingling.
"Where Medical Information is Easy to Understand"™
Pain, tingling, and weakness of the arm can occur if the nerve that
sends impulses to the arm is being pressed on. Pain and stiffness of
the neck can occur if the disk prolapse is in the neck. The symptoms
of disk prolapse are often made worse when the person sneezes,
coughs, sits for long periods, twists the back, or tries to lift heavy
objects.
In rare cases, the disk presses on the spinal cord, leading to
paralysis (loss of movement and/or sensation) of the legs. Pressure
on the spinal cord can also lead to a loss of the control bladder
function and bowel function.
WHERE DOES DISK PROLAPSE USUALLY OCCUR?
In 95% of cases, disk prolapse occurs in the lower back. However, disk prolapse can occur anywhere in
the spine, such as the neck area.
WHAT CAUSES DISK PROLAPSE?
Disk prolapse is sometimes caused by a sudden stressful action upon the back. This is often caused by
lifting a heavy object or twisting the back suddenly and/or violently. Disk prolapse usually occurs slowly as
a result of the disks wearing away with age.
AT WHAT AGE ARE PEOPLE MOST LIKELY TO GET DISK PROLAPSE?
The age at which people are most likely to suffer from disk prolapse is between 30 and 40. This is
because the disks start to lose their fluid content over age 30 and become less resistant to the effects of
stress. However, after age 40, extra tissue forms around the disks, which gives them more support.
ARE MEN MORE LIKELY TO GET DISK PROLAPSE THAN WOMEN?
Yes. Disk prolapse is slightly more common in men than women. There are various possible reasons for
this. One possibility is that disk prolapse is more common in people who sit for long periods without a
break. Men may be more likely to do this than women.
HOW IS DISK PROLAPSE DIAGNOSED?
The doctor will perform various tests to determine what is causing the pain in the back or neck area. The
doctor will likely begin by examining the spine and testing movements and reflexes of the spine, arms, and
legs. The doctor may also arrange for tests to be done so he/she can look at pictures of the spine.
Examples of such tests include an X-ray and a CT (computerized tomography) scan. CT scanning is an
advanced imaging technique that uses x-rays (a type of energy) and computer technology to produce
more clear and detailed pictures than a traditional x-ray.
Another commonly used imaging technique is a myelography. In a myelography, a colored dye is injected
into the fluid that surrounds the spinal cord, making this area more visible on an x-ray. Yet another
technique is called a discography. In a discography, the colored dye is actually injected into the disk so
that the disk shows up more clearly on the x-ray. An electromyography is sometimes used as well. This
test measures the electrical activity of muscles around the spine.
To confirm the exact location of a nerve that is being pressed on by a disk, the doctor may inject a pain-
numbing medication into the area of the back or neck where the pain is located. If this technique reduces
the pain, the doctor can be reasonably sure that this is the area where the problem lies.
HOW IS DISK PROLAPSE TREATED?
Almost all doctors will try to treat disk prolapse without surgery at first. Disk prolapse usually responds well
to bed rest, in which the person lies flat on his/her back on a firm mattress. The hips, ankles, and
shoulders should be aligned to relieve pressure on the spine. Bed rest is usually done for a few weeks. A
supportive collar, supportive garments, and special exercises (as instructed by the doctor) can be helpful.
If these techniques fail, an operation may be needed to relieve the pressure on the nerve. Operations are
most likely to be performed if muscle function is impaired.
WHAT IS THE PROGNOSIS FOR PEOPLE WITH DISK PROLAPSE?
In most cases, the pain will go away when treatment occurs without surgery. However, the pain tends to
come back.
WHAT IS THE ORIGIN OF THE TERM, DISK PROLAPSE?
Disk prolapse comes from the Greek word "diskos" meaning "flat plate," and the Latin word "prolapsus"
meaning "falling." Put the words together and you have "falling flat plate."